Accounting Theories Construction
Good theory would have 3 aspects
/ elements, they’re consists of:
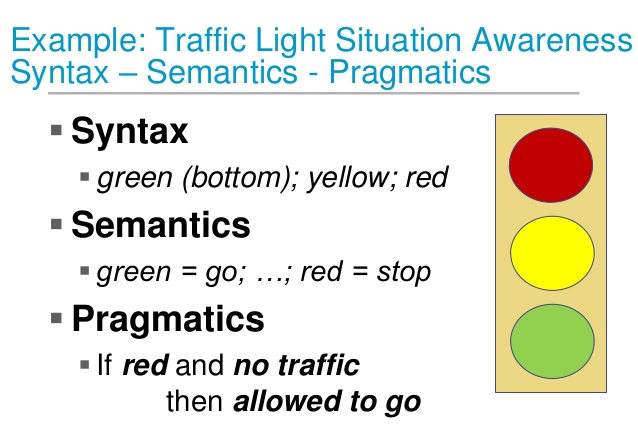
- Semantic theory (ability to relate to the real world)
- Syntactic theory (must be logical)
- Pragmatic theory (observation of accountant behavior in practice)
To ensure that the HCA (Historical
Cost accounting) that have been used in accounting practice can be accepted as
a good theory. It has to be conformed at least one elements of a good theory as
stated above.
Semantic theory
The elements of "Semantic" in HCA
is basically refers to the input of the HCA which have been verified to the
real world by an Auditors. The components of accounting inputs such as
vouchers, journals and ledgers of the business.
Auditors only have a duty to
verify the semantic inputs by checking the calculations and manipulations in
the double entry accounting. But the results of output in Financial Statements
such as profit figure, assets & liabilities figures et cetera can’t be
verified and reflex to the real world by the auditor.
It shows that managements or
stakeholders that uses the information of financial statements are sometimes
can’t rely 100% on the unverified output because sometimes the results of their
decision making is not the same as what they expected. (Refer case Enron).
Conclusion: Therefore HCA is failed to fulfill
the Semantic theory extent in the scope of output verification.
Syntactic theory
The most components of HCA is "Syntactic theory", it means that the logical aspect of syntactic theory is
to the extent of all scope of accounting
system including input and output of the accounting system, the process and its
procedures. It is completely denying the semantic components because as long as
it is logical, there is no need to verify both inputs and outputs in the real
world. But, there are some criticism that shows that the HCA is somehow cannot
be conforms 100% logical.
The criticism of HCA in syntactic
theory:
#1 Summing up 2 same category of assets in the
different timeframe.
Example: adding
a freehold land today with 20 years ago freehold land which is illogical unless
the currency value is always the same as 20 years ago and today. But it is
impossible because of the inflation of economics.
#2 Problems of doublethink (by Chambers)
- Define as holding contradictory beliefs in one’s mind simultaneously, and accepting both of them. Example:
- Valuations are incorporated in balance sheets … but the balance sheet is not a valuation statement.
- Fixed assets should be carried at cost … in HCA, unless such cost is no longer meaningful.
#3 Imprecision of definition (Popperian
approach)
- Depreciation for the year:
- measurement expressed in monetary terms of the physical deterioration within the year, ordecline in monetary value within one year, or
- Indeed of anything actually occurs within the year, or
- Depreciation depends on allocation, which in turn depends on a future sale (disposal price) and expected useful life of the assets which are uncertain and can’t be verified.
- Determination of cost and profit:
- is a choice among conventions, or
- Present magnitude depends on future magnitude.
- Under this logic, true profit cannot be determined until the firm has been liquidated.
Pragmatic (practical) theories
Consists of 2 types:
- Descriptive pragmatic approach
- Psychology pragmatic approach
Descriptive pragmatic approach
Definition:
- Inductive approach
- Oldest & most universally used method of accounting theory approach
- Based on theorists observes an accountants’ behaviour in practice, and learning by copying what accountants did.
- For example; future accountants will learn accounting skills by becoming apprentice in accounting firm and from senior accountant.
Pragmatic test:
test in term of whether and how
people will use them
Sterling (a normative theorist) comments:
He called this method as
anthropological approach. For example; Anthropologist has observed that
accounting man normally records a conservative figure and generalized this as
the principle of conservatism. Test can be done by observing whether or not the
accounting man does the same.
- It doesn’t include analytical judgement (not questioning the quality of accounting work)
- It doesn’t challenge accounting technique & therefore not allowed for change
- Focuses on accounting behavior not measuring the attributes of the firm, assets, liabilities & profits as it is not concerning about semantics of accounting phenomena.
Conclusion from sterling:
The approach isn’t appropriate
for accounting construction as pragmatic theory hasn’t related to normative
theories of how accounting should be conducted rather than describing real
world practices.
Psychological pragmatic approach
Definition:
Based on theorist observes the
user (accountant’s output) reaction @ responses approach. If the user reacts
positively, then the information is useful
Problem arose:
- If the user reacts in illogical manner – the information is not useful
- If the user doesn’t reacts at all – theorist can’t get any conclusion from it.
Conclusion:
Theorists can’t get any far with
this approach.
My Conclusion at The End:
HCA is a theory made that have a lot of weaknesses, despite of it, it still being used as a practice as today. It is significantly out from semantic aspect in verifying the output.
Even in syntactic approach that seemingly logical in all aspects of the accounting system, it also has a lot of criticism by a normative theorists such as summing up amount of a particular assets that has 2 different time frame, problems of doublethink, and an imprecise definition.
Therefore, accountants (positive theorists) seems have a favour in the Pragmatic approach, which is just taking all of the knowledge from the past by observing from the practice and behaviour of an accountant.
P/S: next week, we'll need to know who are Normative theorists and Positive theorists and how are they contribute in the construction of an accounting theory including HCA. Better stay tuned and subscribe to my channel.
No comments:
Post a Comment